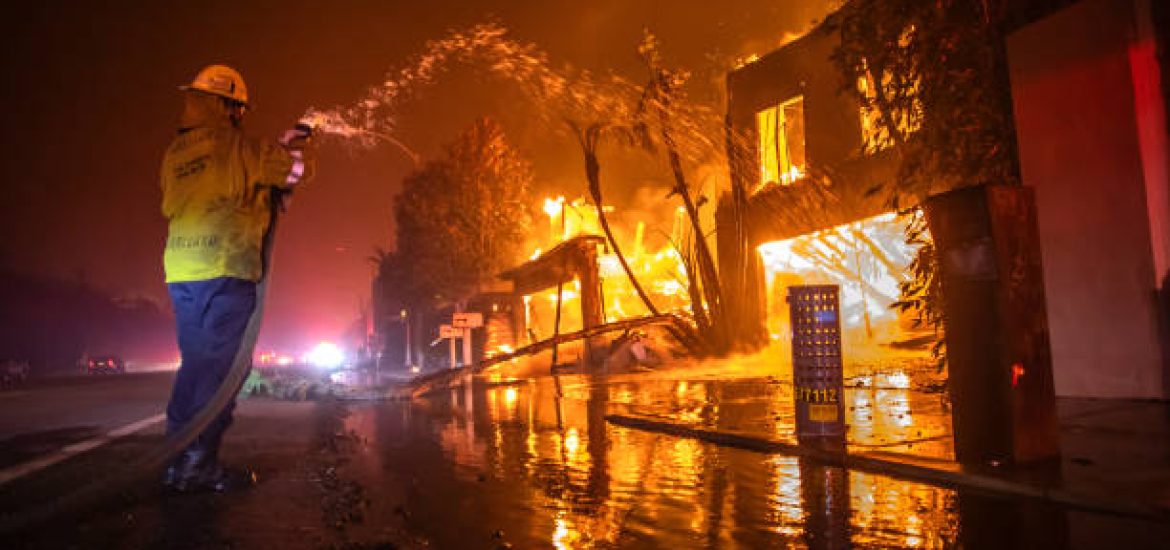
As extreme weather events become more frequent and severe, wildfires, hurricanes, and floods are forcing thousands to abandon their homes. The devastating wildfires in Los Angeles are just one example of how climate change is reshaping communities and displacing people. But where do these climate refugees go, and what does the future hold for those who have lost everything?
Wildfires: A Growing Threat in California
In recent years, California has seen a dramatic increase in wildfires. According to the National Interagency Fire Center, over 2.5 million acres burned in California in 2023 alone, with thousands of homes destroyed. The LA wildfires have particularly affected lower-income communities, where residents often lack the resources to rebuild or relocate. Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts have made the region more susceptible to these disasters, turning what were once rare occurrences into a seasonal crisis.
The Rise of Climate Refugees
The term “climate refugee” is becoming more relevant as extreme weather forces people to flee their homes. The Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre reported that in 2023, over 3 million Americans were displaced due to climate-related disasters. Many of these individuals face an uncertain future, struggling to find stable housing, employment, and support systems.
Unlike traditional refugees fleeing war or persecution, climate refugees do not have formal recognition under international law, making it harder for them to receive aid. With wildfires in California becoming more destructive each year, this issue is only expected to worsen.
Where Do They Go?
For many displaced by wildfires, the first step is temporary shelters set up by relief organizations. However, these are short-term solutions, and long-term housing remains a major challenge. Some people relocate to other parts of California, but high housing costs make it difficult for many to resettle. Cities like Phoenix, Las Vegas, and Denver have seen an increase in climate migrants looking for a fresh start, though these areas are not immune to extreme weather themselves.
Some families move to less disaster-prone states, such as Minnesota or Ohio, where housing is more affordable, and the risk of wildfires is lower. However, moving across the country comes with its own challenges—finding jobs, rebuilding communities, and adapting to new environments can be overwhelming.
The Economic and Social Impact
Climate displacement is not just an environmental issue; it has major economic and social consequences. When wildfires destroy entire neighborhoods, local economies suffer. Businesses shut down, job opportunities vanish, and infrastructure takes years to rebuild. Displaced individuals often experience financial hardship, with many falling into poverty due to the loss of their homes and livelihoods.
On a broader scale, cities receiving large numbers of climate refugees must adapt to increased housing demands, rising costs, and greater pressure on social services. Without proactive planning, these migrations could strain resources and create further social inequalities.
What’s the Solution?
Addressing climate displacement requires a multi-faceted approach. Governments must invest in wildfire prevention strategies, such as controlled burns and improved forest management. More affordable housing solutions are needed to accommodate those who lose their homes. Additionally, there should be stronger legal protections and financial support for climate refugees to help them rebuild their lives.
As extreme weather events intensify, climate refugees will only increase. While wildfires rage in California today, hurricanes, floods, and rising sea levels threaten other regions worldwide. It’s time to take action, not just to prevent disasters but to support those who are forced to flee in their wake.